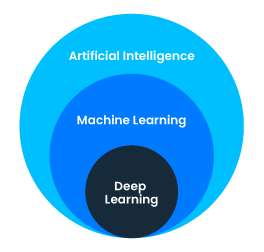
Artificial Intelligence vs Machine Learning vs Deep Learning
When we hear the term Artificial Intelligence, we often think of a robot or a computer that can function independently. AI is more than that; it’s machines learning, processing info, and making decisions.
AI can use to automate processes, analyze large datasets, and even develop creative solutions to complex problems. By 2030, the global economy expects AI to contribute $15.7 trillion. This amount is greater than the combined annual output of China and India.
In addition, what is the state of Machine Learning and Deep Learning? Are they the same as Artificial Intelligence or not? Let’s discuss them individually and discuss their impact on our lives.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
What comes to mind when you imagine a machine thinking and responding accordingly? That is actually Artificial Intelligence or AI. As the word suggested, Artificial means man-made, and intelligence means the ability to understand things. In artificial intelligence, a machine can do tasks instead of human intelligence.
For example, AI-based technologies such as facial recognition, natural language processing, and robotics are being used to improve many tasks, from healthcare to customer service. AI is the broader term in which Machine Learning and Deep Learning lie. Let’s have a look at them too.
What is Machine Learning (ML)?
Machine Learning is part of Artificial Intelligence. It provides information to the computer using past data or experiences and improves accordingly. You can achieve this without needing specific programming.
ML systems use historical data to identify patterns, make predictions, or optimize processes. Examples of Machine Learning include spam filtering, facial recognition, recommendation systems, and self-driving cars.
What is Deep Learning (DL)?
Deep Learning is a subset of Machine Learning. It uses information from neural networks and mimics like a human brain. These neural networks comprise multiple layers of interconnected nodes (neurons) that process and transform data at each layer. Examples of Deep Learning include natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, speech recognition, and robotics.
Artificial Intelligence vs Machine Learning vs Deep Learning
When we hear the term Artificial Intelligence, we often think of a robot or a computer that can function independently. AI is more than that; it’s machines learning, processing info, and making decisions.
AI can use to automate processes, analyze large datasets, and even develop creative solutions to complex problems. By 2030, the global economy expects AI to contribute $15.7 trillion. This amount is greater than the combined annual output of China and India.
In addition, what is the state of Machine Learning and Deep Learning? Are they the same as Artificial Intelligence or not? Let’s discuss them individually and discuss their impact on our lives.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
What comes to mind when you imagine a machine thinking and responding accordingly? That is actually Artificial Intelligence or AI. As the word suggested, Artificial means man-made, and intelligence means the ability to understand things. In artificial intelligence, a machine can do tasks instead of human intelligence.
For example, AI-based technologies such as facial recognition, natural language processing, and robotics are being used to improve many tasks, from healthcare to customer service. AI is the broader term in which Machine Learning and Deep Learning lie. Let’s have a look at them too.
What is Machine Learning (ML)?
Machine Learning is part of Artificial Intelligence. It provides information to the computer using past data or experiences and improves accordingly. You can achieve this without needing specific programming.
ML systems use historical data to identify patterns, make predictions, or optimize processes. Examples of Machine Learning include spam filtering, facial recognition, recommendation systems, and self-driving cars.
What is Deep Learning (DL)?
Deep Learning is a subset of Machine Learning. It uses information from neural networks and mimics like a human brain. These neural networks comprise multiple layers of interconnected nodes (neurons) that process and transform data at each layer. Examples of Deep Learning include natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, speech recognition, and robotics.
Impact on Businesses and Society
- AI, ML, and DL tech automate industries and boost efficiency and productivity. Businesses streamline tasks, optimize supply chains, and improve decision-making with these technologies.
- AI recommendation systems are changing how businesses connect with customers. Companies can offer personalized content, products, and services by studying user preferences and behavior, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- AI and ML assist businesses in analyzing big data and obtaining valuable insights rapidly. This aids in making data-based decisions, recognizing market trends, and forecasting customer behavior.
- AI in healthcare improves patient outcomes by analyzing medical images, discovering new drugs, and developing personalized treatment plans.
- AI, ML, and DL have pros and cons. They can improve things but also bring worries like privacy, biased algorithms, and job loss.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence’s rapid evolution is transforming our world significantly. New technologies are improving industries. They make operations more efficient, give customers personalized experiences, and extract valuable insights from large amounts of data.
Recognizing their potential, it is important to address ethical concerns. This is necessary to ensure responsible adoption and maximize their positive impact on businesses and society. AI, ML, and DL are shaping our lives and technology, bringing innovation and progress to create an exciting future.







